Relying on third party code (libraries, modules, packages, frameworks, etc) to make building software easier has been the norm for the better part of a decade. But over that same time period, managing those third party dependencies has not gotten any easier since they still:
- Break the build
- Pose security risks, and
- Eat up development time building them from source code, remediating their vulnerabilities, managing the conflicts that inevitably arise, ensuring environment reproducibility, and so on.
Software best practices can help your teams avoid most of the common, third-party dependency pitfalls by encouraging:
- Loose coupling of your code to third-party dependencies
- The use of abstractions wherever possible
- Avoiding deprecated interfaces
- Using similar (or as similar as possible) sets of dependencies across dev, test and production environments, and
- Avoiding specific dependency versions, where possible.
Of course, these aren’t really dependency management solutions—more like dependency mitigation techniques that can help you minimize the amount of time your developers require to manage their dependencies.
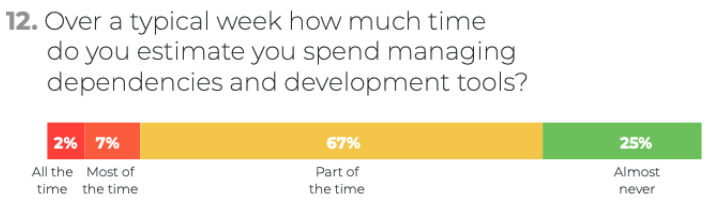
Like it or not, though, every development team needs to dedicate some of their time to dealing with the low value, non-differentiating work of managing your dependencies instead of working on high-value features and functionality. This was made clear in a 2019 developer survey we ran, which asked devs at organizations worldwide both big and small:
Only one-quarter of developers manage to avoid spending their precious velocity points dealing with dependencies. Handled poorly, dependencies can hamstring your organization, but if handled well, they can empower your developers. One way to help minimize the time three-quarters of your developers spend on dependency management is to provide them with automated solutions.
Dependency Management Automation Tools
The transition from talking about code reuse to TINA (There Is No Alternative) seemingly happened overnight, probably sometime around 2014 when the US Government finally threw in the towel and adopted open source software despite their security concerns. Since then, there have been a number of software vendors that have promised to make the process of dependency management easier by providing automated tools to deal with:
- Policy-based dependency enforcement (or else a repository of dependencies) to help ensure developers aren’t adding dependencies that haven’t been approved for use.
- Vulnerability identification so you can understand the security risk your current software poses.
- Vulnerability mitigation by suggesting recent versions of the dependency that have fixed the vulnerability.
- License compliance by helping you understand how your current dependencies are licensed.
- Build services that can help build the dependency from source code, ensuring security and integrity.
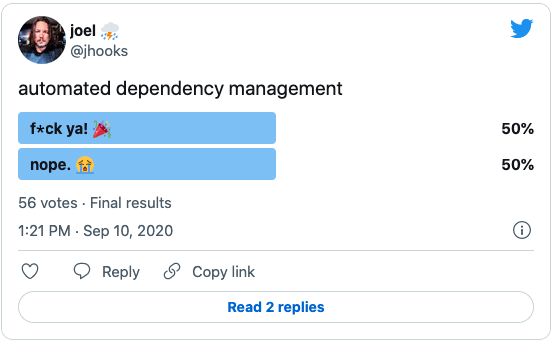
While these features sound great, the reality of using them looks more like a flood of emails about updates, vulnerabilities and PRs opened on your behalf, which is just adding to your workload rather than resolving it. It’s why developers often have a divisive reaction when they hear the phrase “automated dependency management” as shown in the following Twitter poll results:
Automation is only good as the amount of work it can help take off your plate. Otherwise, it’s just noise. All of which is why I’ve spent the last few weeks introducing how the ActiveState Platform automates common dependency management tasks, including:
- Vulnerability detection and remediation
- Dependency conflict resolution
- Runtime environment creation
- Environment reproducibility
- Eliminating “works on my machine” issues
- Environment restoration / recoverability
- Dependency builds from source code, including like C/Fortran libraries
- Artifact repository population
None of these features require language or OS expertise on behalf of the user, and they automate many of the most difficult tasks from compiling C and Fortran libraries for multiple OS’s to suggesting workarounds to dependency conflicts.
See how the ActiveState Platform works:
Next steps:
Of course, even automated solutions are only useful if your teams have the time and resources to implement and make use of them. After all, reliable dependency management comes not only from using the right tools, but also applying them in conjunction with best practices. Enterprises have relied on ActiveState to provide both for more than 20 years.
All of the automated dependency management solutions in this post are also available as a managed service, which can free up your developers to focus on coding and getting your product to market faster. To learn more about our Managed Builds service: